Can an Administrator Launch the Group Policy Management Console From a Workstation?
Group Policy (GP) is a Windows management characteristic that allows you lot to control multiple users' and computers' configurations inside an Agile Directory environment.
With GP, all Organizational Units, sites, or domains can exist configured from a single and central identify.
This characteristic helps network admins in big Windows environments to save fourth dimension past non having to become through every computer to set a new configuration.
Although there are other means to manage Windows estates, similar Desired State Configuration (DSC), Organization Centre Configuration Manager (SCCM), and Mobile Device Management (MDM), nothing allows the fine-grained control that GP provides.
What is the Group Policy Management Console?
A collection of Group Policy (GP) settings, referred to as a Group Policy Object (GPO), determines how a grouping of users or computers must acquit.
GPOs are associated with AD containers, including the local computer, site, domain, and Organizational Unit (OU).
Grouping Policies within the entire Advertising wood can be managed via the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC)— a built-in Windows Server 2008 (and beyond) admin tool.
GPMC works via the Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-in.
It consolidates the functionality of many tools (snap-ins) into one, including the Advertising Users and Computers, Resultant Set of Policy, the ACL Editor, and the GMPC Delegation Wizard.
Overall, GPMC gives you the interface to view, control, and troubleshoot GPs from a central place.
Merely you lot tin besides have a fine-command to create GPOs that define policies, security options, software updates, installation, maintenance settings, scripts, folder redirections, and more than.
Additionally, y'all can also fill-in, restore, and import GPOs.
To open up GPMC, go to the Windows Server Manager > Open up "Tools Carte" > "Group Policy Direction"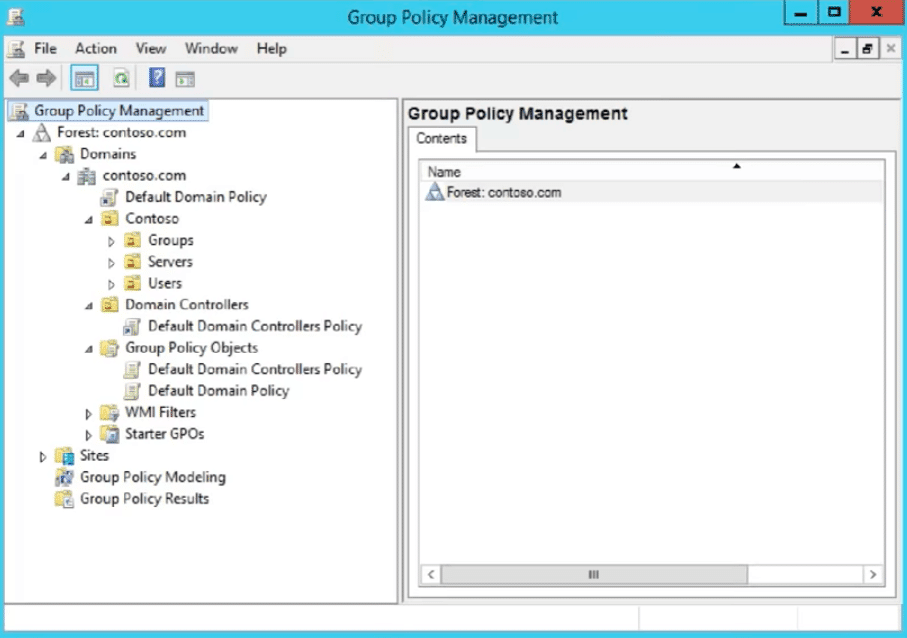
How to Install the Group Policy Direction Console?
As mentioned before, GMPC is born in Windows Server (starting from 2008), so installing information technology is a very straightforward process.
In this tutorial, we'll install the GPMC on a Windows Server 2012 R2.
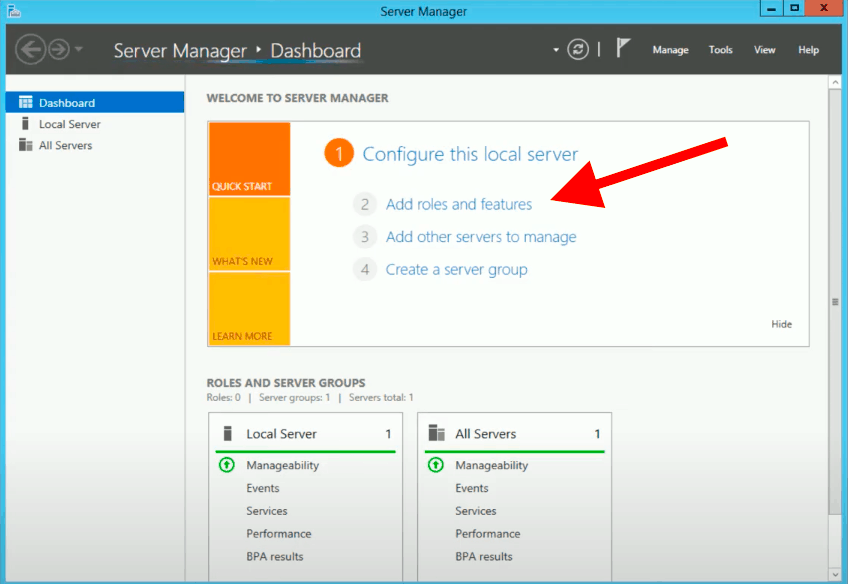
- Open the Server Manager. Past default, the Server Manager application is pinned downward at the taskbar. But if yous can't observe it there, yous can agree the combination of Win + R keys to open the Run window. Then type "Server Managing director" and click "Ok."
- In Server Manager's dashboard, click "Add together roles and features."
- The Add together Features and Roles Wizard will open.
Leave the "Installation Blazon" with its default values: "Role-based or Feature-based installation."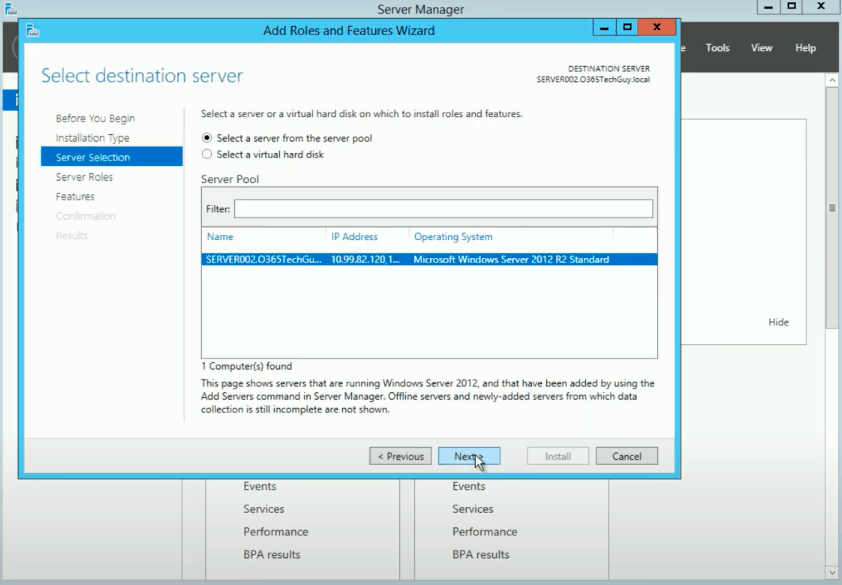
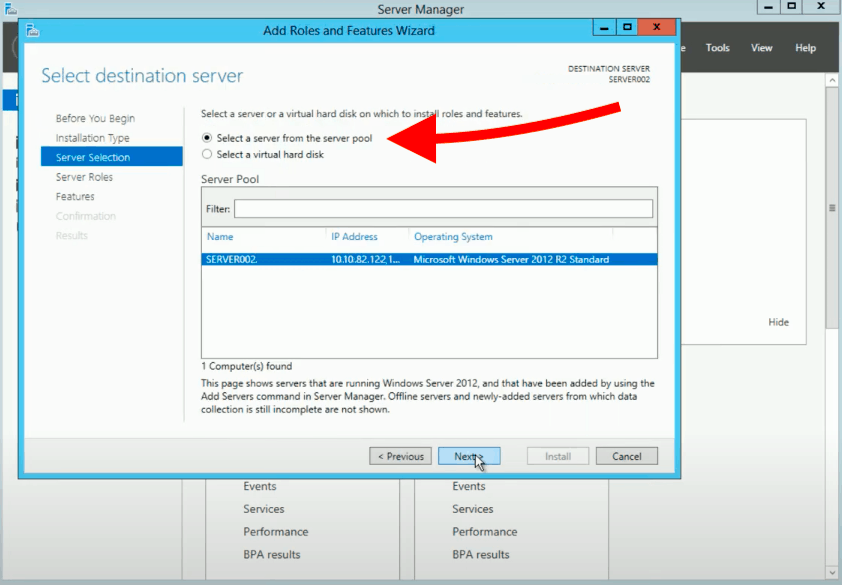
- Select a server from your server pool.
Observe the server running Windows where y'all want to install the GPMC. Click "Next."
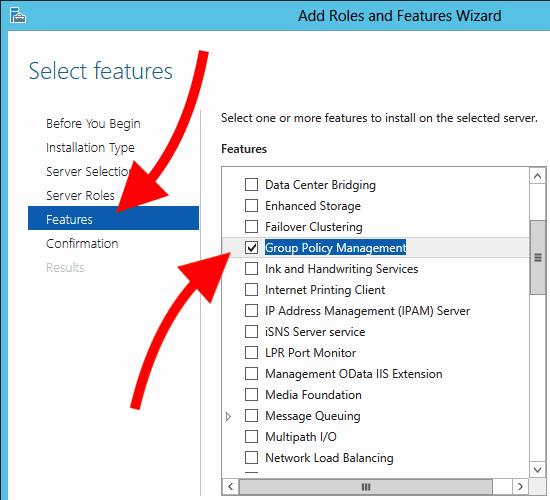
- Skip Server Roles and Go to "Features." In the "Features" section, you lot should find the "Group Policy Management" tool. Go ahead, tick the box, click "Next," and click on "Install."
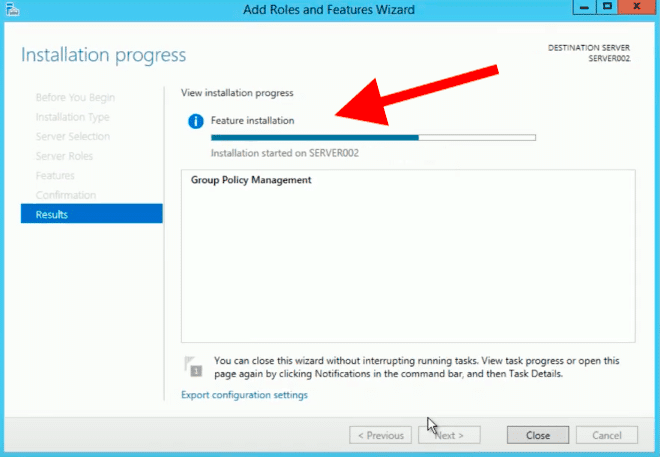
- The installation process should accept a few minutes to complete.
How to employ the Group Policy Direction Console?
To open GPMC, go again to the Administrator Tools (Win + R and blazon "Administrator Tools"), detect and double-click on the Group Policy Direction Console.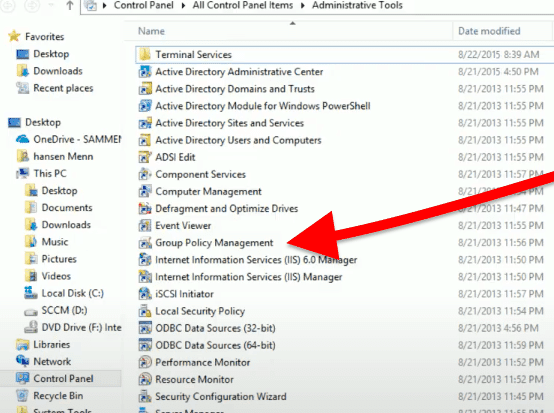
As mentioned earlier, the Group Policy Management Console allows y'all to manage the entire Advert forest, including its sites, domains, and Organizational Units.
- To run across the inventory of all GPOs configured nether a Domain: Get to the left pane of the GPMC.
- Under "Forest": Select the "Domain" > and go to "Group Policy Objects."
- Here, yous'll notice 2 types of default GPOs: The Default Domain Policy and the Default Domain Controllers Policy. One is linked to the domain, and the other to the domain'due south controller.
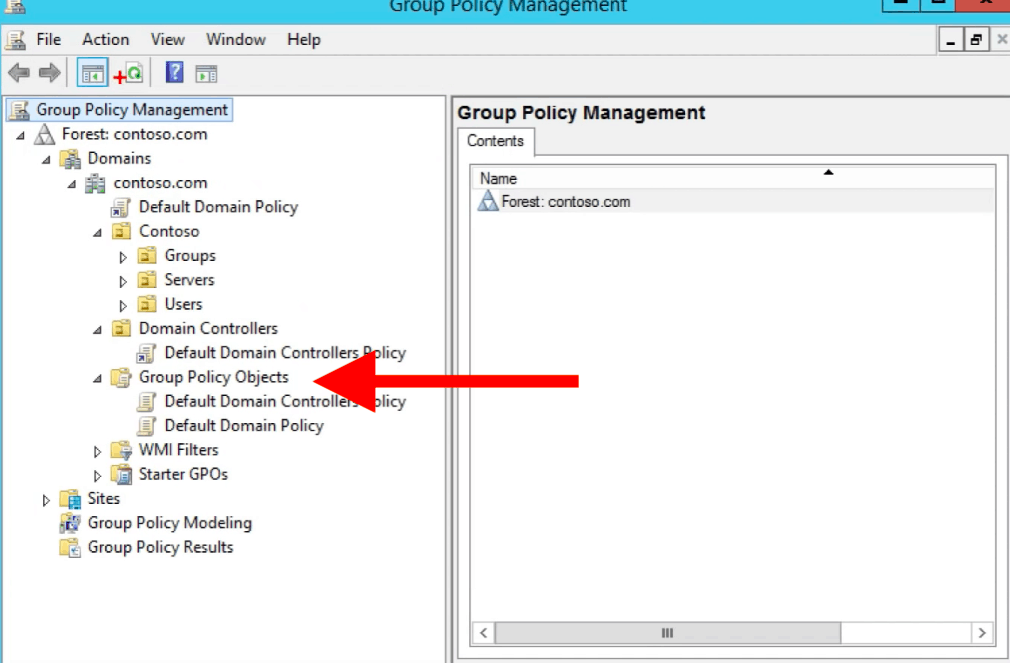
Within this construction, including Domain Controllers and Domains'south policies, you lot tin can see the status of their GPOs, linked GPOs, GP Inheritance, and their Delegation.
How to Create a New Group Policy Object (GPO)?
Equally a best practice, avoid irresolute Default Domain Policy and Default Domain Controllers Policy, as you can always take GPOs back to their original configuration.
There are a few things you need to consider when creating a new GPO.
- Requite your new GPO a name (you tin utilise some other GPO's proper noun every bit a Source).
- Determine where to link your new GPO, whether OU, domain, or site.
To create a new GPO:
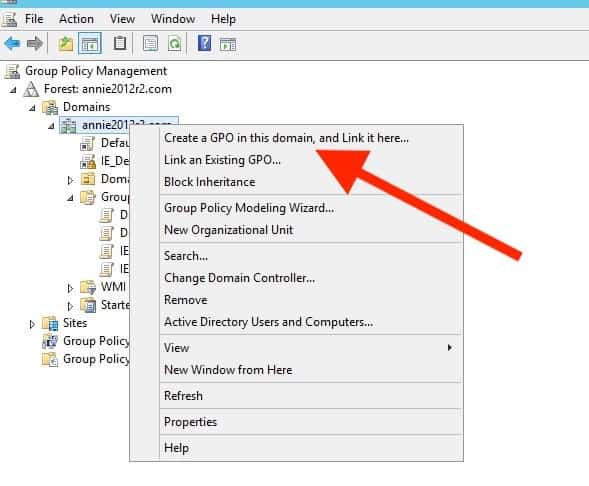
- Right-click on the OU, and click on the option "Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here…"
- Give your new GPO a Proper noun, and click "Ok."
- When y'all save it, your brand new GPO will be instantly enabled and linked to the specified OU.
The second way to create a new GPO is to right-click on the Grouping Policy Object container and click on "New." Your new GPO is created but un-linked!
Using this 2nd method, you'll accept to manually link the new GPO to a domain, site, or OU. Right-click where you want to link it, and select "Link an Existing GPO."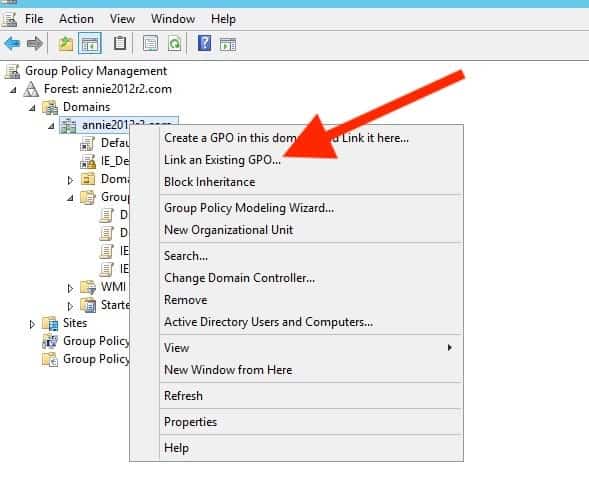
Once you create the new GPO, it will instantly be linked, enabled, and stored in the GPO inventory.
How to Edit a Group Policy Object?
Once you create a new GPO for any domain, site, or OU, information technology volition be automatically generated with default configuration values. These values take no configuration whatsoever, then you'll need to open up the GPO and edit its "default" configuration.
To edit a GPO, go to the GPO inventory and find the GPO that you want to edit, right-click on information technology and select "Edit."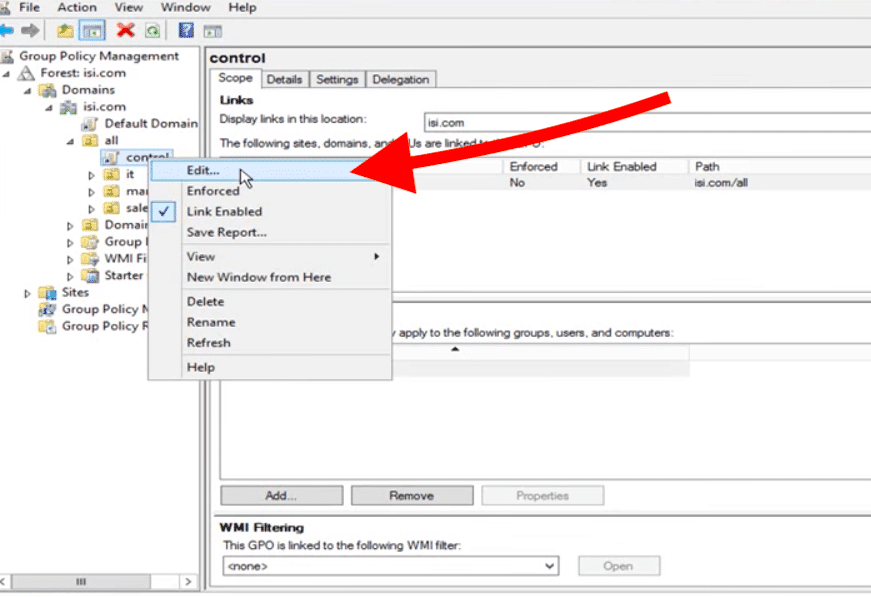
The Group Policy Management will automatically open up on the editor in a new window.
The Group Policy Direction Editor is also an essential Windows admin tool that allows users to change configuration policies on computers and users.
The structure of the editor is divided into two GPO configuration types: "User" and "Estimator."
The user configuration is set when the user logs in, whereas the computer configuration applies to the Windows OS when it starts.
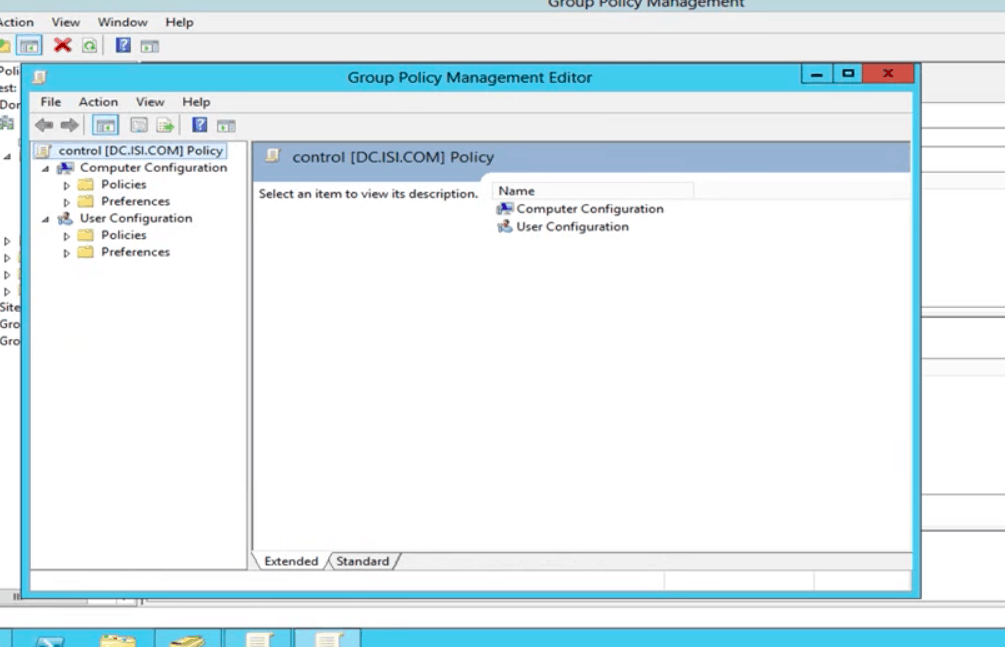
GPO Configuration: Policies and Preferences
The GPM Editor'south structure is farther divided into Policies and Preferences, whether you are nether User or Computer configurations.
What are their differences?
- Policies:
Started since Windows Server 2000. Policies accept been the original method on how we configure settings globally. When a policy is applied to a computer or user, configurations may exist changed or removed, simply they'll go back to their value equally defined in the Group Policy. These settings accept more priority than the application's configuration settings, and sometimes they even "grayed out." Inside policies, you'll find Software Settings (apply software configuration to computers/users), Windows Settings (for Windows security or accounting settings), and Administrative Templates (Control of the Os and user).
Policies are checked and applied every 90 minutes through a procedure called "Groundwork Refresh"
- Preferences:
This setting was included since Windows 2008 with the thought to replace the login custom scripts that were used to add functionality. These settings can be applied, only if desired, and are not "policied" with a background refresh (as policies do). Preferences are set only when a figurer starts, or the user logs for the first fourth dimension, but let the user more flexibility to change and remove them.
Within Preferences, you tin can prepare the Windows settings and Control Panel Settings. Preferences can just be configured within domain GPOs, whereas policies tin can be set for both domain and local GPOs.
GPO Precedence and Inheritance
Equally mentioned previously, when you create a new GPO, yous also need to link information technology somewhere, such as domain, site, or OU.
Simply you tin also have multiple GPOs linking to different domains, sites, or OUs. Only to allow this, you'll demand to ready priorities.
The GPO Precedence allows GPOs to exist configured with different levels of priorities.
Past default, the GPOs with the almost precedence are those linked to the OU. Bottom precedence goes to those linked to the domain and then to the site.
The least amount of precedence is given to local group policies. That means the GPOs linked to an OU in AD's highest level will exist candy first.
- To see the GPOs linked to a specific domain, site, or OU, go to the Linked Group Policy Objects tab.
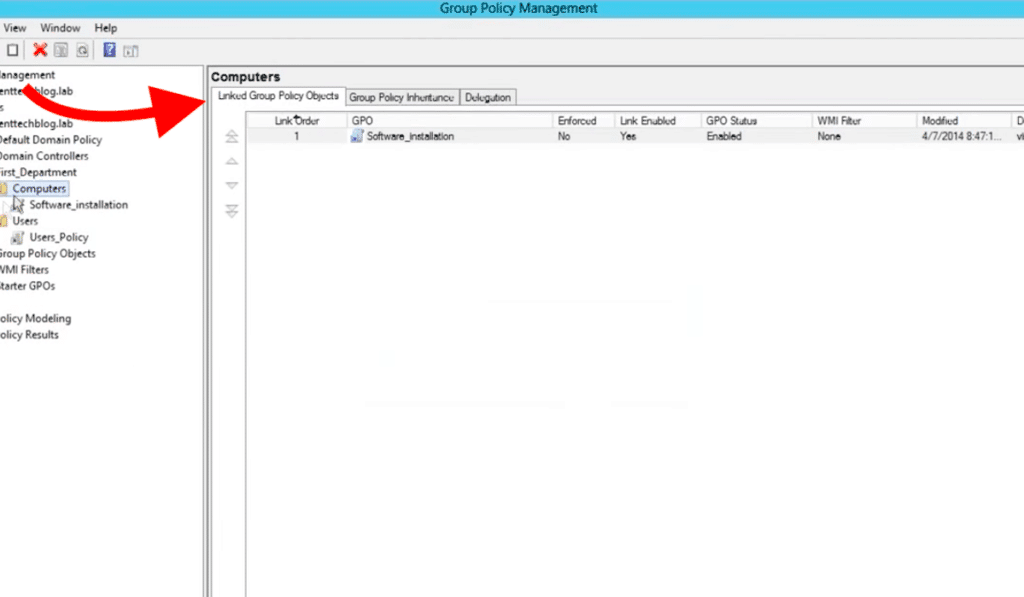
If in that location is a single GPO linked, you should see information technology in this tab. If there are more, you will see all GPOs with their respective Link Order number.
The highest the link number a GPO has, the least precedence information technology has.
For example, a GPO with a Link Order No. of 1 volition always have precedence over a GPO with Link Order No.2.
To adjust the GPO precedence, you can change the Link Social club number by moving the GPO upwardly or downward.
By default, all grouping policy settings linked to a parent object (i.due east., site, domain, or OU) are inherited to the child objects (domain, OUs, or kid OU) within the AD hierarchy.
Y'all tin encounter all the inherited GPOs from the Group Policy Inheritance tab.
Final Words
When configuring group policies, Microsoft'due south Group Policy Management Panel (GPMC) is a must!
While other third-party Group Policy management tools can likewise help you command GPs, with extraordinary capabilities, cypher compares to GPMC.
The GPMC is the out-of-the-box Windows Server tool.
It is easy to install and use. GPMC is non just made to create and edit GPOs; you can have exceptional fine-grain control and even automate things.
For instance, If you are looking for automation while staying in the Windows environment, GPMC likewise includes the PowerShell module.
This module will assist you automate management tasks for your Grouping Policies.
Related Postal service: All-time Active Directory Monitoring Tools & Software
Source: https://www.pcwdld.com/group-policy-management
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Can an Administrator Launch the Group Policy Management Console From a Workstation?"
Posting Komentar